The initial consultation lasts approximately 30 minutes. This varies according to the condition and it could last longer, if needed. During the consultation the patient will be asked about their medical history and current problem. They could also bring previous scans or other tests relevant to their condition, as well as previous medical reports. If there is a referral from a GP or another specialist this is also useful.
In order to provide a thorough examination some additional procedures may be needed in the consulting room. These could be:
Rigid Sinus Endoscopy
During this procedure the doctor uses a small instrument with a light on the end in order to examine the internal and back of the nose, sinuses as well as the openings of the Eustachian tubes. It also involves placing a camera in the nose in order to diagnose conditions and carry out minor outpatient procedures.
This is one of the best methods to investigate problems with mouth, throat, oesophagus and trachea. It is also used to locate masses, lumps, polyps or tumours.
Before the use of the rigid endoscope the patient receives a local anaesthetic in the form of spray.
Flexible fibreoptic laryngoscopy
The flexible endoscope is used for the diagnosis of conditions, such as sore throat, difficulty swallowing, voice problems, upper oesophagus, hypopharynx, pharynx and larynx issues, post nasal drip and neck lumps.
A local anaesthetic in the form of spray is also performed before this examination. The flexible scope is passed through the nose and into the throat.
Microsuction of the ear
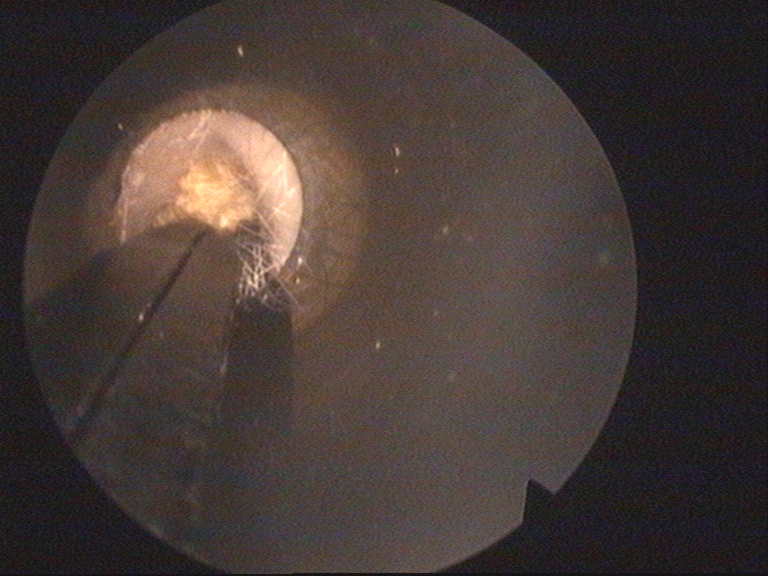 In order to diagnose and treat conditions of the ear, such as itchy ear, otitis externa, ear infection, ear discharge, ear wax or hearing loss a binocular operating microscope is used.
In order to diagnose and treat conditions of the ear, such as itchy ear, otitis externa, ear infection, ear discharge, ear wax or hearing loss a binocular operating microscope is used.
This procedure may be noisy and a bit painful. However, it provides great relief as it unblocks the ear canal.


